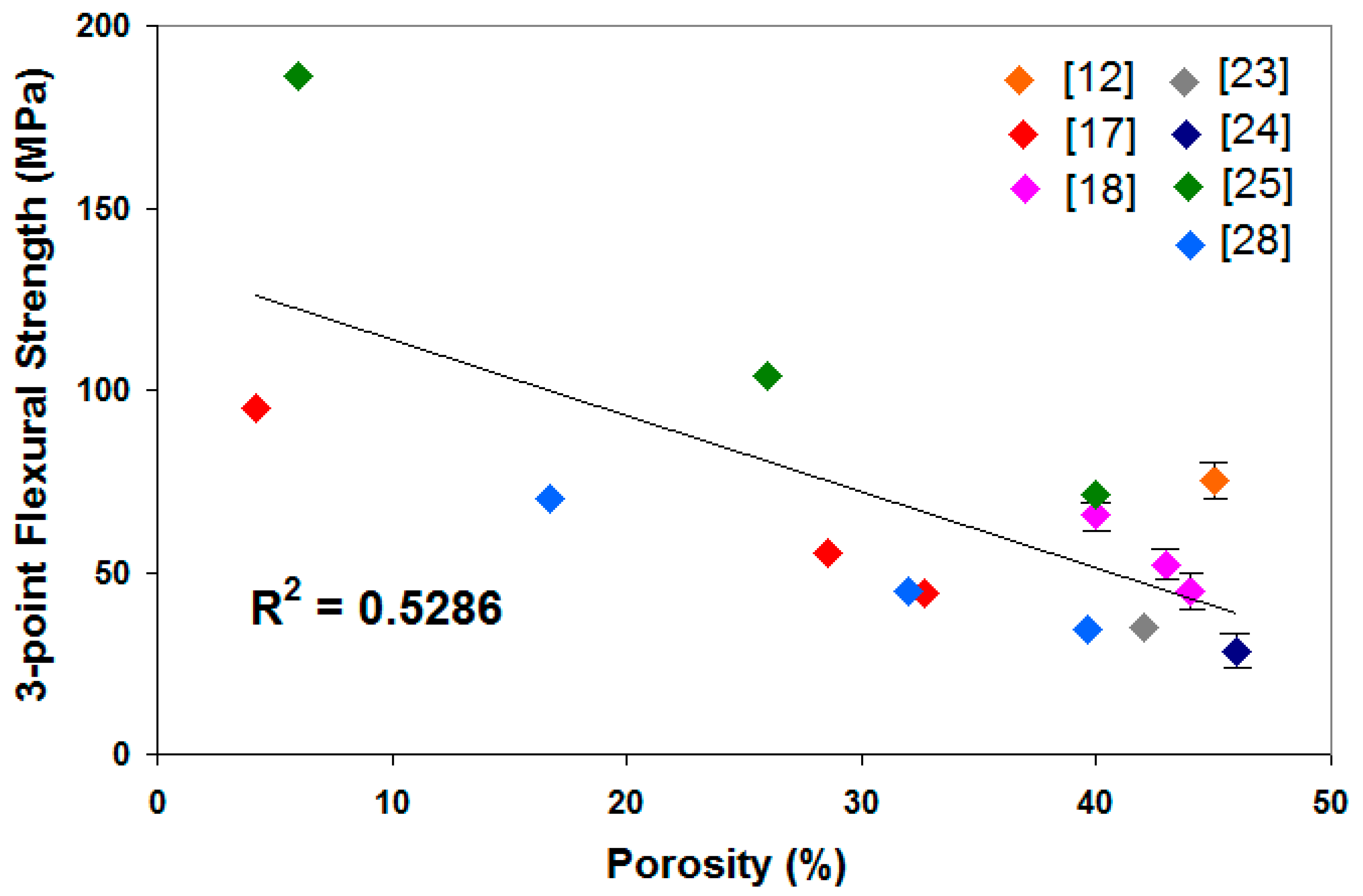
Porous ceramics were prepared by different methods to achieve pore volume fractions from 4 to 95.
Thermal conductivity of very porous kaolin based ceramics.
The effective thermal conductivity of a porous material is due to both conduction and radiation processes.
Thermal conductivity of very porous kaolin based ceramics by julie bourret aurélie michot nicolas tessier doyen benoît nait ali fabienne pennec arnaud alzina jerome vicente claire peyratout and david stanley smith.
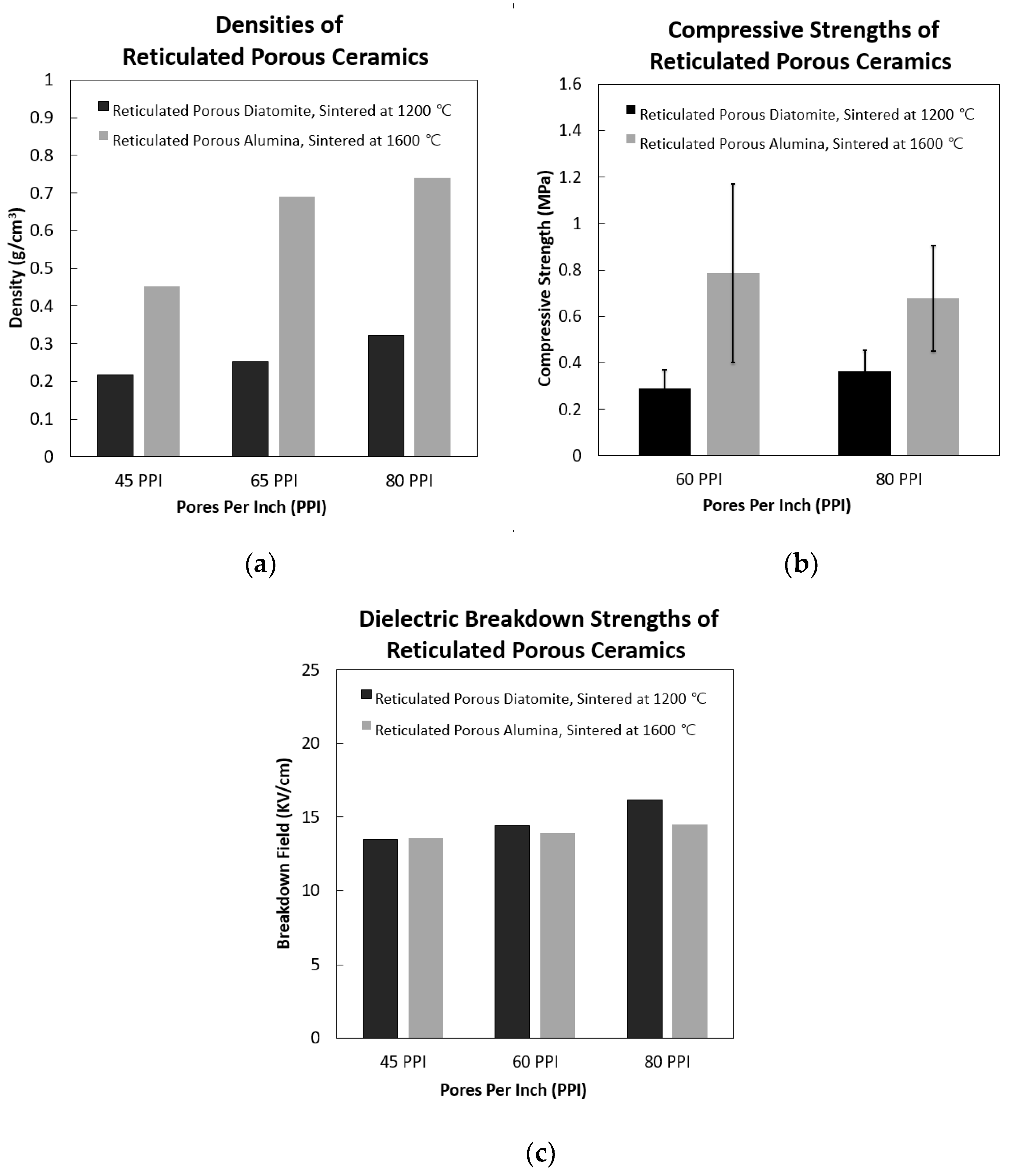
Obtained porous ceramics from al 2 o 3 poly hollow microspheres.
A toolbox of analytical relations is proposed to describe the effective thermal conductivity as a function of solid phase thermal conductivity pore thermal conductivity and pore volume fraction ν p.
Thermal treatment of the kaolin foam at 1100 c yields a suitable compromise between low thermal conductivity of 0 054 w m k 1 at room temperature with a compressive yield stress of 0 04 mpa.
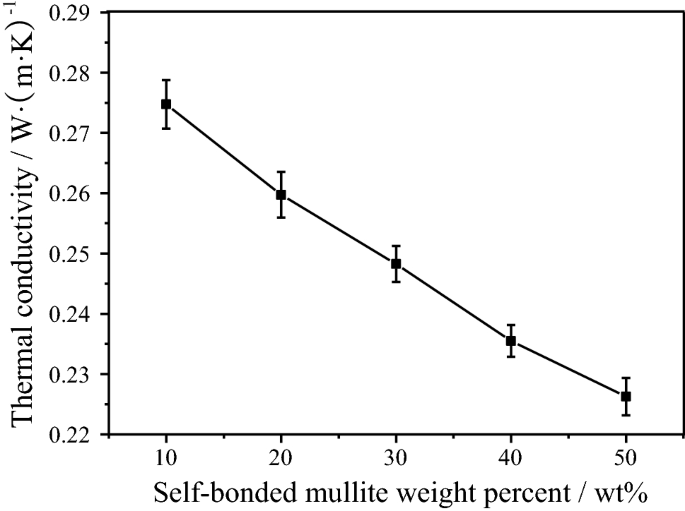
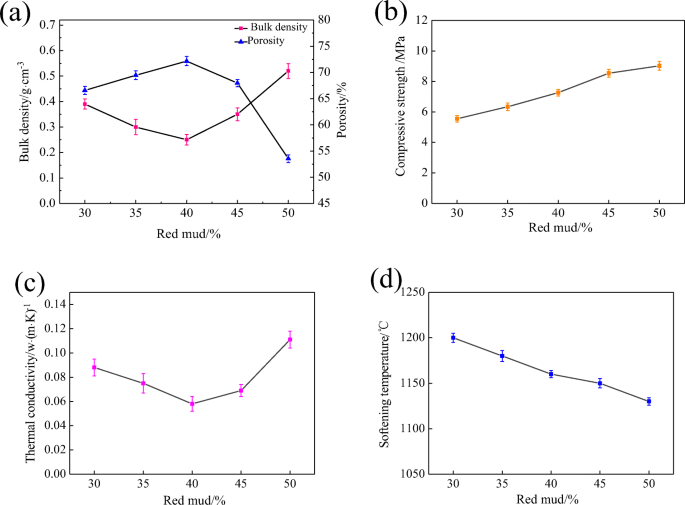
Hence developing low cost porous mullite ceramics with high mechanical performance low thermal conductivity and good dielectric properties is very important for radome applications.
15 the solid phase of a fired clay building brick that is without porosity exhibits a thermal conductivity between 0 8 and 1 1 w m 1 k 1 at room temperature.
Very porous ceramics based on a commercial clay containing 79 kaolinite were made by a.
Very porous ceramics based on a commercial clay containing 79 kaolinite were made by a.
The radiation component in the effective thermal conductivity is 10 at 20 c increasing to 50 at 500 c.
In this paper a series of high porosity mullite ceramics with overlapped rod like grains were prepared from kaolin as extremely low cost raw material and.
Using a guarded plate method norton obtained values for refractory kaolin bricks at 400 c ranging from 0 6 to 2 2 w m 1 k 1.
Candidate materials for thermal insulation combine a solid phase of low thermal conductivity with porosity.
Very porous ceramics based on a commercial clay containing 79 kaolinite were made by a direct foaming method using methylcellulose drying at 70 c before a consolidation at 1100 c.
The casio 3 as sintering additive coating microspheres via the coprecipitation method which improved the mechanical properties of the obtained porous ceramic.
A theory is presented relating the effective conductivity to the conductivity of the solid material to the emissivity of the surface of the pores and to the size shape and distribution of the pores.
Candidate materials for thermal insulation combine a solid phase of low thermal conductivity with porosity.