Epdm sheet rubber is a versatile blended sheet epdm sheet rubber is a versatile blended sheet composed of ethylene propylene diene monomer and styrene butadiene rubber.
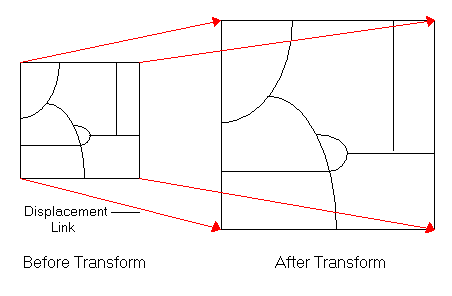
Spatial adjustment rubber sheet.
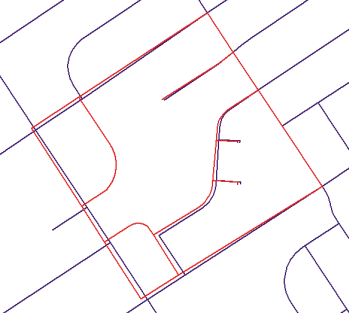
You will rubber sheet a newly imported set of street features to match an existing feature class of street features.
You can switch from an affine to a similarity or a projective transformation or a rubber sheet adjustment in spatial adjustment main drop down menu by choosing adjustment method.
It achieves an ideal balance to create an all purpose weather resistant rubber.
Various technical terms have actually been used with regard to scts in practical problems for instance spatial adjustment image registration absolute orientation geo referencing and frame.
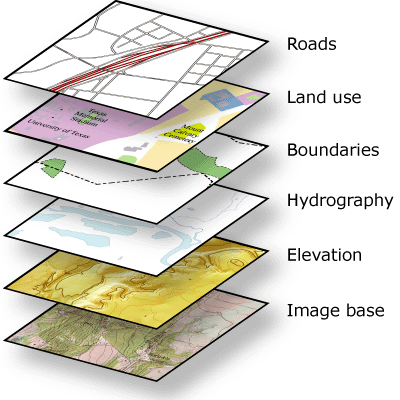
Gis data often comes from many sources.
You can experiment with affine similarity and projective transformations and or rubber sheeting to see the differences and to choose which one does the best job of.
The spatial adjustment functions provide the ability to transform rubber sheet edgematch and transfer attributes within your data.
Inconsistencies between data sources sometimes require you to perform additional work to integrate a new dataset with.
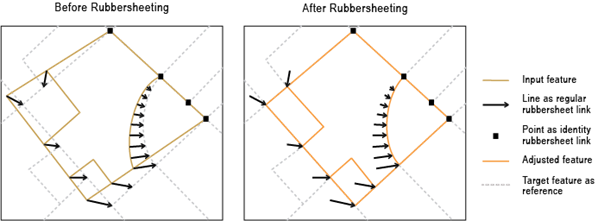
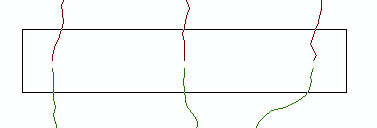
The input point features represent identity links that hold source positions unmoved during the rubbersheeting process.
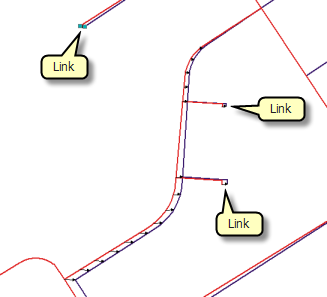
The input link features represent the regular links.
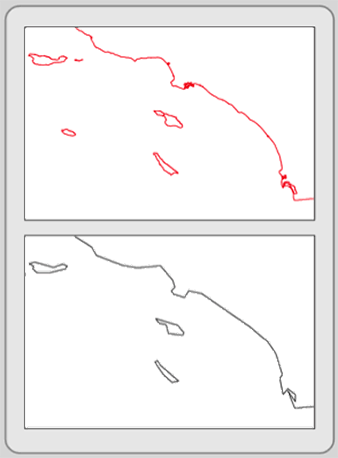
Rubber sheeting spatial adjustment of a feature class in arcgis.
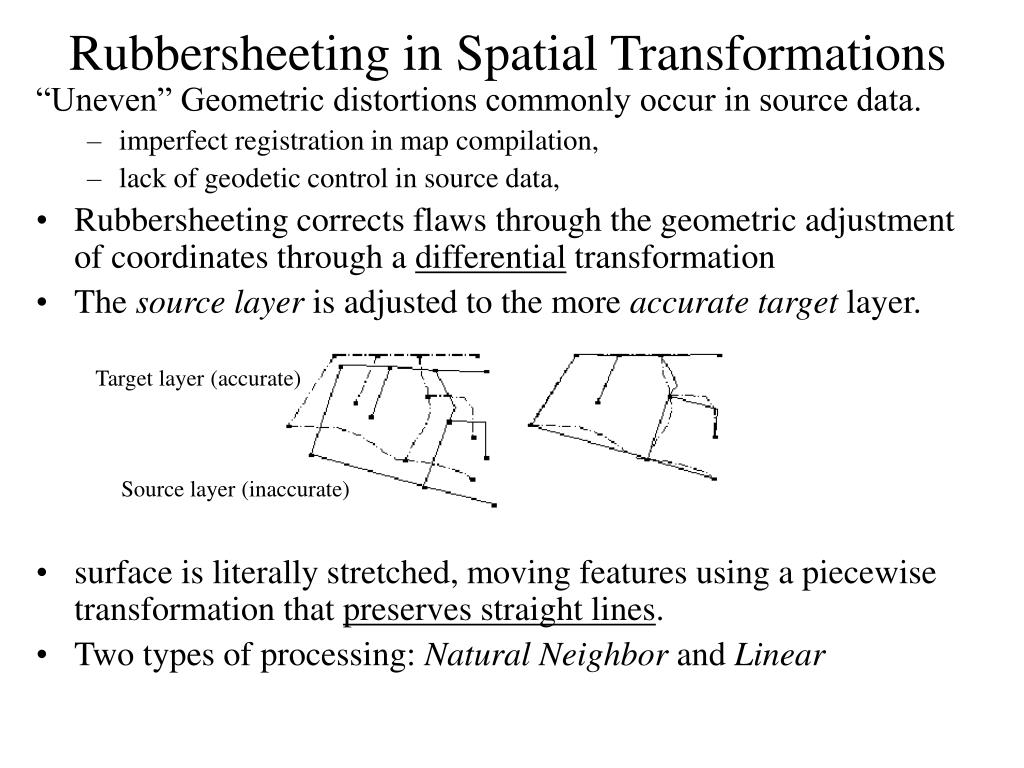
For example you can use rubbersheeting to update utility data in a geometric network to reflect changes in the underlying land base data.
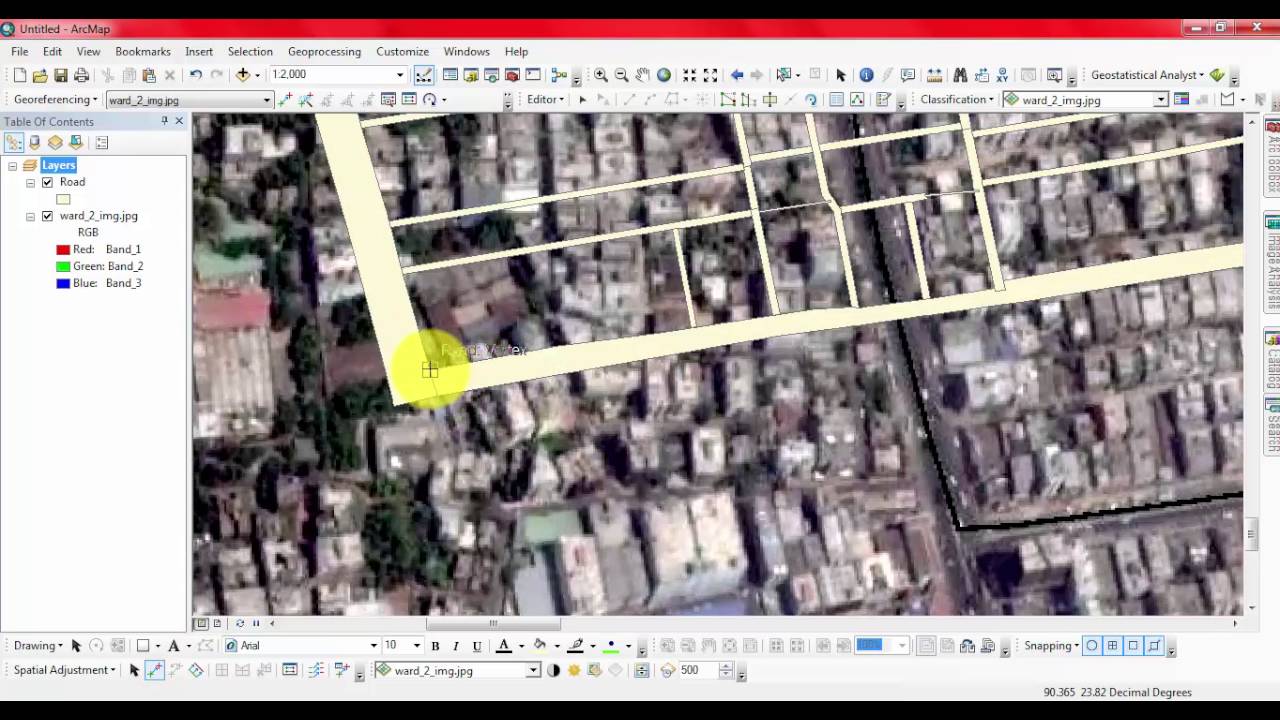
Start arcmap and display the editor snapping and spatial adjustment toolbars.
For this reason epdm material is an excellent medium for outdoor uses.
It is important to note that the spatial adjustment process will only work against geometric network junctions so you should.
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
It is important to note that the spatial adjustment process will only work against geometric network junctions so you should.
For example you can use rubbersheeting to update utility data in a geometric network to reflect changes in the underlying land base data.
You can perform spatial adjustments on data participating in a geometric network.
All these functions occur within the current edit session and if used via a graphical user interface gui are enclosed within an edit operation.
You can perform spatial adjustments on data participating in a geometric network.
Setting up the data and rubbersheeting options prerequisite.